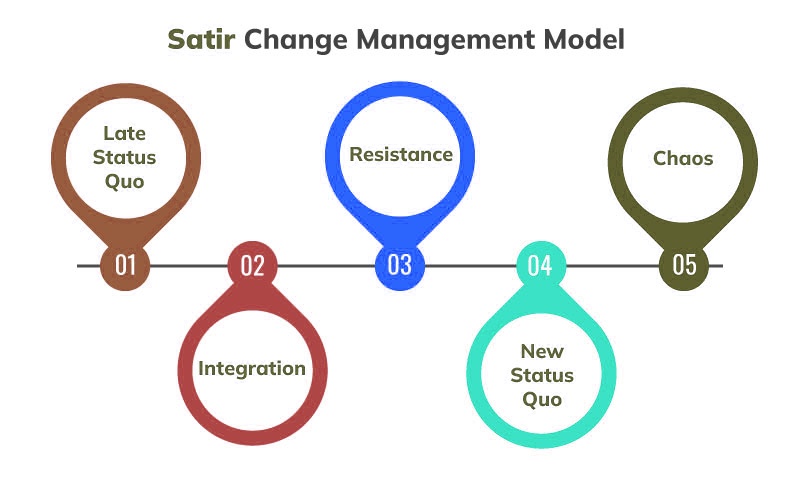
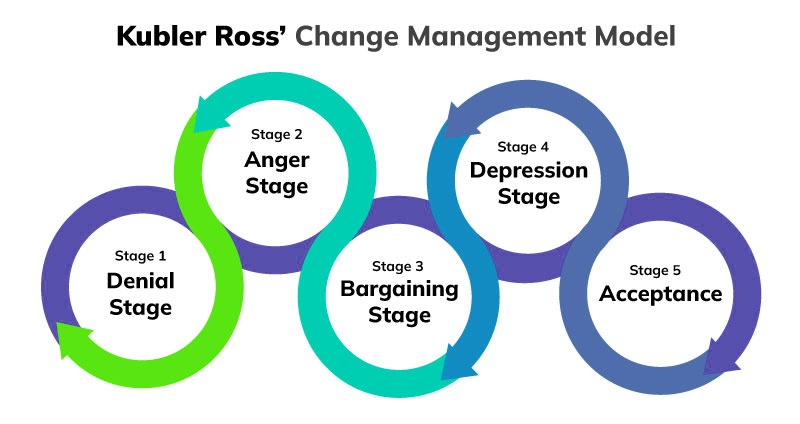
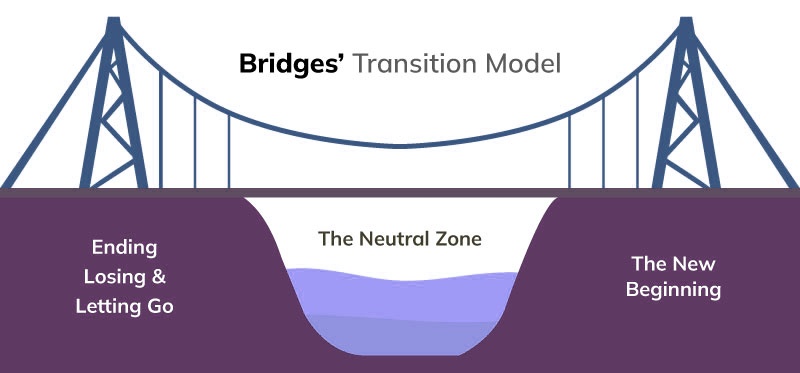
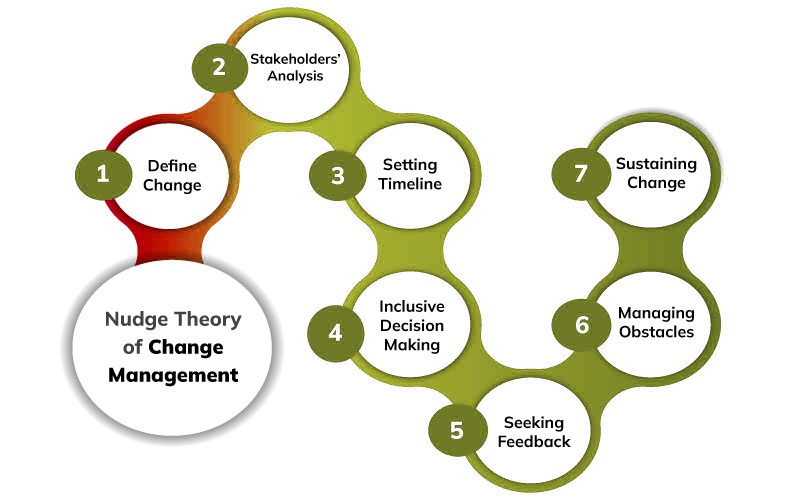
Overview
In 2024, academic research continues to push the boundaries of knowledge across diverse fields, offering insights into pressing global challenges and emerging trends. This blog highlights the top five academic research topics poised to make significant impacts this year, spanning from advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning to breakthroughs in sustainable energy, health innovations, social sciences, and the exploration of outer space. These topics not only reflect the interdisciplinary nature of modern research but also underscore the collective efforts of scholars worldwide in addressing complex issues and shaping the future of academia and beyond. Let’s explore some of the trending academic research topics for 2024:
Table of Contents
The consequences of obesity
This thesis delves into the consequences of obesity, shedding light on the multifaceted effects it has on individuals' health and the broader societal implications. With a focus on accessible language, this research aims to provide valuable insights for healthcare providers, policymakers, and anyone keen on understanding the challenges associated with obesity.
Chapter 1: Defining Obesity and Its Prevalence
1.1 Definition of Obesity: We start by clarifying what obesity means, emphasizing the excessive accumulation of body fat and its classification based on Body Mass Index (BMI).
To begin our discussion, it's crucial to clarify the concept of obesity, a medical condition characterized by the excessive accumulation of body fat. This condition goes beyond mere weight gain, involving an intricate interplay of genetic, environmental, and behavioral factors. A key metric used to classify obesity is the Body Mass Index (BMI), calculated by dividing an individual's weight in kilograms by the square of their height in meters. Specific BMI thresholds are employed to categorize individuals into different weight status classifications. While BMI is a widely accepted measure, it is essential to recognize its limitations, such as not accounting for variations in muscle mass or distribution of fat.
Understanding obesity as the result of an imbalance between calorie intake and expenditure is fundamental. The consequences of obesity extend beyond aesthetic concerns, significantly impacting overall health and well-being. By emphasizing the definition of obesity and its classification through BMI, we set the stage for a more in-depth exploration of its causes, consequences, and the imperative for proactive interventions.
1.2 Global Prevalence: Exploring the widespread nature of obesity, highlighting its global prevalence and the increase in obesity rates over time.
The widespread nature of obesity has evolved into a global health challenge, with its prevalence surging over the years. According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), the global prevalence of obesity has nearly tripled since 1975. In recent times, more than 1.9 billion adults are categorized as overweight, with over 650 million classified as obese. This escalation is not confined to high-income countries but spans diverse socioeconomic backgrounds and geographical regions.
The rise in obesity rates is attributed to a complex interplay of factors. Globalization has brought about shifts in dietary patterns, with an increased consumption of processed foods high in sugars and unhealthy fats. Sedentary lifestyles, marked by decreased physical activity and increased screen time, further contribute to this upward trend. Rapid urbanization, changes in food environments, and cultural shifts towards more sedentary occupations collectively foster an environment conducive to weight gain.
Understanding the global prevalence of obesity underscores the need for a comprehensive and collaborative approach on an international scale. By acknowledging the widespread nature of this issue, policymakers, healthcare professionals, and communities can work together to implement effective strategies that address the root causes and mitigate the impact of obesity on a global level.
Chapter 2: Health Consequences of Obesity
2.1 Physical Health: Discussing the impact of obesity on physical health, including conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and joint problems, and the strain it puts on various organs.
Obesity significantly impacts physical health, contributing to a range of adverse conditions that pose substantial risks to overall well-being. One of the most notable consequences is the increased likelihood of cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension, coronary artery disease, and stroke. The excess body weight associated with obesity puts additional strain on the heart, leading to elevated blood pressure and an elevated risk of heart-related complications.
Obesity is also a major risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes. The body's ability to regulate insulin becomes compromised, leading to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism. This not only poses immediate health risks but also increases the likelihood of long-term complications such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Musculoskeletal issues, particularly joint problems like osteoarthritis, are prevalent among individuals with obesity. The additional weight places increased stress on weight-bearing joints, accelerating wear and tear and contributing to pain and reduced mobility. Respiratory issues, such as sleep apnea and decreased lung function, are common due to the impact of excess body weight on the respiratory system.
Beyond these conditions, obesity can strain various organs, leading to complications in the liver, kidneys, and digestive system. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is more prevalent among individuals with obesity, highlighting the systemic impact of excess fat accumulation.
Recognizing the profound impact of obesity on physical health underscores the urgency of comprehensive interventions. Lifestyle modifications, nutritional education, and societal initiatives that promote healthier choices and increased physical activity are essential in alleviating the strain on various organs and mitigating the risk of associated health conditions.
2.2 Mental Health: Examining the connections between obesity and mental health, addressing issues like depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem that can be exacerbated by obesity.
The connections between obesity and mental health are intricate and profound, as individuals grappling with obesity often face additional challenges that extend beyond physical health concerns. One significant aspect is the impact on mental well-being, where obesity is associated with higher rates of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem.
The societal stigma surrounding body weight can contribute to negative self-image and feelings of inadequacy among individuals with obesity. Discrimination, bias, and weight-related bullying can exacerbate emotional distress, fostering an environment that contributes to mental health challenges. Persistent societal pressure to conform to unrealistic body standards can contribute to body dissatisfaction, further impacting mental well-being.
Depression is a prevalent mental health issue associated with obesity. The complex interplay between biological, psychological, and social factors can contribute to the development and exacerbation of depressive symptoms. The challenges of weight management, societal perceptions, and the emotional toll of obesity can contribute to a sense of hopelessness and sadness.
Anxiety is another common mental health concern among individuals with obesity. The fear of judgment, social isolation, or the anticipation of weight-related discrimination can heighten anxiety levels. Moreover, the physiological effects of obesity, such as sleep apnea and compromised respiratory function, can contribute to feelings of unease and anxiousness.
Low self-esteem often emerges as a consequence of the societal pressures and negative perceptions associated with obesity. Individuals may internalize stigmatizing beliefs, leading to a diminished sense of self-worth and confidence.
Addressing the connections between obesity and mental health requires a holistic approach that goes beyond physical health interventions. Comprehensive strategies should encompass mental health support, counseling, and initiatives aimed at reducing weight-related stigma. By fostering a more compassionate and understanding societal attitude, individuals with obesity can be better supported in their mental well-being, promoting a more inclusive and empathetic approach to health and body image.
Chapter 3: Social and Economic Impacts
3.1 Social Stigma: Delving into the societal consequences of obesity, addressing the stigma and discrimination individuals with obesity often face and its impact on mental well-being.
The societal consequences of obesity extend beyond physical health implications and often manifest in the form of stigma and discrimination, significantly affecting the mental well-being of individuals. Weight-based stigma is pervasive in various societal contexts, from educational and workplace settings to interpersonal relationships. Individuals with obesity often encounter prejudice, stereotyping, and discriminatory behaviors, leading to profound emotional and psychological distress.
Weight stigma can exacerbate existing mental health issues and contribute to the development of conditions such as depression and anxiety. The constant fear of judgment, social rejection, or negative perceptions can lead to heightened stress levels and a diminished sense of self-worth. Coping with weight-related stigma may also lead to maladaptive behaviors, including unhealthy eating patterns or avoidance of social situations, further impacting mental well-being.
In educational environments, individuals with obesity may face bullying and teasing from peers, leading to social isolation and a negative impact on academic performance. In the workplace, weight-related discrimination can result in reduced job opportunities, unequal treatment, and limited career advancement, leading to economic and psychological consequences.
Addressing the societal consequences of obesity requires a collective effort to challenge and change prevailing attitudes. Promoting awareness and education to dispel stereotypes, fostering empathy, and creating inclusive environments that celebrate diversity in body sizes are essential steps. Encouraging open conversations about weight-related issues can contribute to reducing stigma and fostering a more supportive and understanding society.
Recognizing the impact of societal consequences on mental well-being emphasizes the need for a compassionate and holistic approach to addressing obesity. By combating weight stigma, society can contribute to the creation of an environment that promotes the mental health and overall well-being of individuals irrespective of their body size.
3.2 Economic Burden: Exploring the economic ramifications of obesity, considering healthcare costs, lost productivity, and the strain on public health resources.
Obesity carries substantial economic ramifications, impacting both individual finances and public health resources on a global scale. Healthcare costs associated with obesity-related conditions form a significant portion of medical expenditures, ranging from preventive measures to chronic disease management. These expenses include hospitalizations, medications, and interventions to address complications such as cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, and orthopedic issues. Moreover, obesity-related conditions contribute to increased demand for medical services, adding strain to healthcare systems and escalating overall expenditure.
Lost productivity constitutes another economic challenge, as individuals with obesity often experience higher rates of absenteeism and decreased on-the-job efficiency. Workplace costs rise due to factors like sick leave, disability claims, and reduced work performance, leading to a notable economic burden on employers and economies at large. Furthermore, the strain on public health resources extends to preventive and educational programs, as well as the need for specialized healthcare infrastructure to address the rising prevalence of obesity.
In light of these economic challenges, comprehensive strategies are essential, focusing on prevention through public health initiatives, promoting healthier lifestyles, and investing in education to mitigate the multifaceted economic impacts of obesity. Addressing this issue holistically can lead to improved overall well-being, reduced healthcare costs, and enhanced productivity in the long term.
Chapter 4: Childhood Obesity
4.1 Early Onset: Discussing the consequences of obesity in childhood, emphasizing the long-term health effects and the importance of early intervention.
Childhood obesity carries significant consequences with profound implications for long-term health. Children affected by obesity face an increased risk of developing various health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory issues. Additionally, obese children often experience musculoskeletal problems, such as joint pain and difficulties with mobility, impacting their overall physical well-being. The psychological toll is also considerable, as children with obesity are more susceptible to depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem due to societal stigmatization and peer-related challenges.
One of the most concerning aspects is the likelihood that childhood obesity persists into adulthood, exacerbating the risk of chronic diseases throughout life. Early intervention is paramount to breaking this cycle, as it can prevent the development of obesity-related health issues and establish healthy habits that may persist into adulthood. Interventions should encompass a combination of nutritional education, physical activity promotion, and support for both children and their families to adopt and maintain healthier lifestyles.
Recognizing the consequences of obesity in childhood underscores the importance of comprehensive and early interventions. By addressing this issue during the formative years, society can mitigate the long-term health effects, improve overall well-being, and set the foundation for healthier future generations.
4.2 Educational Impacts: Addressing how obesity can impact academic performance and overall well-being in children and adolescents.
Obesity significantly affects academic performance and overall well-being in children and adolescents, creating multifaceted challenges that extend beyond physical health. Physiologically, the consequences of obesity, such as sleep disturbances and reduced physical fitness, can impair cognitive function and concentration, hindering academic engagement. Sleep apnea, prevalent in obese individuals, may lead to daytime drowsiness and decreased alertness in the classroom, impacting learning and memory retention.
The psychosocial implications of obesity contribute substantially to academic challenges and diminished well-being. Children and adolescents with obesity often face social isolation, bullying, and weight-related stigma, leading to heightened levels of stress, anxiety, and depression. These emotional burdens can distract from educational pursuits, affecting self-esteem and overall mental health. Negative body image and societal pressures can create an environment where students may struggle with self-confidence, further influencing their academic performance.
Interventions to address the impact of obesity on academic success and well-being should be comprehensive. School-based initiatives should prioritize physical education, nutrition education, and mental health support services. Fostering a positive and inclusive school culture that promotes acceptance and diversity is crucial in mitigating the social stigma associated with obesity. Collaborative efforts involving educators, parents, and healthcare professionals can create environments that support the holistic well-being of children and adolescents, enabling them to thrive academically and emotionally.
Chapter 5: Prevention and Intervention
5.1 Healthy Lifestyle Promotion: Highlighting the significance of promoting healthy lifestyle choices and the role of education in preventing obesity.
Promoting healthy lifestyle choices and prioritizing education play pivotal roles in preventing obesity, fostering long-term well-being, and mitigating the associated health risks. Education serves as a powerful tool to raise awareness about the importance of maintaining a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and overall wellness. By imparting knowledge about nutrition, the impact of sedentary behaviors, and the benefits of an active lifestyle, individuals are empowered to make informed decisions that contribute to their health.
Schools play a crucial role in this process, with curriculum integration and extracurricular activities serving as platforms to instill healthy habits from an early age. Nutrition education programs can provide students with the skills to make nutritious food choices, while physical education initiatives contribute to the development of active lifestyles. These educational efforts extend beyond the classroom, involving parents and communities to create environments that support healthy living.
In addition to formal education, public health campaigns and community programs play integral roles in disseminating information and reinforcing the importance of healthy choices. Governments, healthcare professionals, and advocacy groups can collaborate to implement policies that encourage access to nutritious foods, promote physical activity, and create supportive environments for individuals and families.
By emphasizing education and cultivating environments that prioritize health, society can proactively address the root causes of obesity. Empowering individuals with knowledge and fostering a culture that values and supports healthy choices are essential components of a comprehensive strategy to prevent and combat obesity, contributing to improved public health outcomes in the long run.
5.2 Intervention Strategies: Discussing potential intervention strategies, both at the individual and societal levels, to address and mitigate the consequences of obesity.
Effective intervention strategies for addressing and mitigating the consequences of obesity should encompass a multi-faceted approach, targeting both individuals and society as a whole. At the individual level, education plays a central role. Promoting nutritional literacy and encouraging the development of healthier eating habits through programs in schools, workplaces, and healthcare settings can empower individuals to make informed choices about their diets. Similarly, fostering physical activity through accessible and enjoyable exercise options, whether in schools, communities, or workplaces, is crucial for maintaining a healthy weight.
Behavioral interventions that focus on goal-setting, self-monitoring, and building sustainable habits can aid individuals in achieving and maintaining weight loss. Support systems, such as counseling and group interventions, can provide emotional and psychological assistance, addressing the mental health aspects associated with obesity.
On a societal level, public health policies are instrumental in creating environments conducive to healthier lifestyles. Implementing regulations that limit the marketing of unhealthy foods, promoting the availability of nutritious options, and incentivizing physical activity can contribute to shaping a healthier food landscape. Additionally, community-based programs, such as farmers' markets and initiatives that enhance urban planning for walkability and recreational spaces, encourage active living.
Addressing social determinants of health, including socioeconomic factors, is vital for reducing health disparities related to obesity. Collaborative efforts involving healthcare professionals, policymakers, educators, and community leaders can amplify the impact of interventions. By creating an environment that supports and encourages healthy choices while addressing the root causes of obesity, these comprehensive strategies have the potential to effectively mitigate the consequences of obesity at both the individual and societal levels.
Chapter 6: Conclusion
6.1 Comprehensive Understanding: Summarizing the key points discussed and emphasizing the need for a comprehensive understanding of obesity to develop effective strategies for prevention and intervention.
In summary, addressing obesity requires a comprehensive understanding of its multifaceted nature, involving physical, mental, and societal factors. The consequences of obesity encompass a range of health issues, impacting individuals from childhood through adulthood. Physically, obesity contributes to chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and joint problems, while also affecting mental health, leading to issues like depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. The economic implications are substantial, involving healthcare costs, lost productivity, and strain on public health resources.
To develop effective strategies for prevention and intervention, a multi-level approach is essential. At the individual level, education and behavioral interventions can empower people to make healthier choices, fostering sustainable lifestyle changes. On a societal level, public health policies, community-based programs, and efforts to address social determinants of health are critical components. Recognizing the interconnectedness of these factors and promoting a holistic understanding of obesity will lead to more impactful and enduring solutions. By combining individual empowerment with societal changes, we can create environments that support healthy living and effectively mitigate the consequences of obesity on a global scale.
6.2 Call to Action: Issuing a call to action for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals to work collaboratively in addressing the consequences of obesity and fostering a healthier society.
A call to action is essential in the collective effort to address the consequences of obesity and pave the way toward a healthier society. Healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals must unite in a collaborative endeavor to tackle the multifaceted challenges posed by obesity. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in educating and guiding individuals toward healthier lifestyles, emphasizing preventive measures, and offering support for sustainable weight management.
Policymakers must enact and advocate for initiatives that create environments conducive to healthier living. This includes implementing regulations to promote nutritious food options, restricting the marketing of unhealthy products, and investing in community-based programs that encourage physical activity. Addressing social determinants of health and promoting health equity should be integral to these efforts.
On an individual level, it is imperative for everyone to take an active role in their health. By making informed choices about nutrition, engaging in regular physical activity, and seeking support when needed, individuals can contribute to their well-being and that of their communities.
This collaborative approach, spanning healthcare, policy, and individual actions, is the key to fostering a healthier society and mitigating the consequences of obesity. Together, we can create an environment that supports and promotes healthy choices, ultimately leading to improved physical and mental well-being for individuals and communities around the globe.
Wrap Up: In conclusion, this thesis contributes to a broader understanding of the consequences of obesity, providing valuable insights for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals committed to promoting health and well-being on both individual and societal levels.
The influence of Social Media
This thesis delves into the profound influence of social media on individuals and society at large. In an era dominated by digital connectivity, platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and others have become integral parts of our daily lives. The research aims to provide a holistic understanding of how social media shapes our thoughts, behaviors, relationships, and societal dynamics.
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Background: Social media has transformed the way we communicate, share information, and build connections. Understanding its impact is crucial for navigating the digital landscape effectively.
1.2 Objectives: This study seeks to analyze the multifaceted influence of social media, addressing both positive and negative aspects, to contribute to a more nuanced comprehension of its role in contemporary society.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Social Media and Communication: Exploring how social media platforms facilitate communication, breaking geographical barriers and fostering global connectivity.
2.2 Influence on Personal Identity: Examining how individuals construct and express their identities through social media, and the potential impact on self-esteem and self-perception.
2.3 Impact on Relationships: Investigating the effects of social media on interpersonal relationships, friendships, and romantic connections, considering both the strengthening and weakening aspects.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1 Research Design: Utilizing a mixed-methods approach, combining surveys, interviews, and content analysis to gather comprehensive data on social media usage and its impact.
3.2 Sample Selection: Ensuring diversity in age, gender, and cultural background to capture a broad spectrum of experiences and perspectives.
Chapter 4: Findings
4.1 Positive Influences: Highlighting the ways social media contributes to information dissemination, community building, and empowerment, fostering positive changes in society.
4.2 Negative Influences: Exploring the darker side of social media, including issues such as cyberbullying, privacy concerns, and the potential for misinformation to spread rapidly.
Chapter 5: Discussion
5.1 Balancing Act: Discussing the need for individuals and society to strike a balance between harnessing the benefits of social media and mitigating its negative impacts.
5.2 Ethical Considerations: Addressing the ethical implications of social media usage, emphasizing the importance of responsible digital citizenship.
Chapter 6: Conclusion
6.1 Key Insights: Summarizing the main findings and their implications for individuals, communities, and policymakers.
6.2 Future Directions: Suggesting avenues for future research to deepen our understanding of the evolving landscape of social media and its impact on society.
In conclusion, this thesis contributes to a broader comprehension of the influence of social media, shedding light on its complexities and offering insights for navigating the digital age responsibly.
Economic development and happiness
In this thesis, we dive into the relationship between economic development and happiness, seeking to understand how a growing economy impacts the joy and satisfaction of individuals. This exploration is vital for policymakers and economists striving to create conditions that not only boost financial prosperity but also contribute to the overall happiness of a society.
Chapter 1: Defining Economic Development and Happiness
1.1 Economic Development: We begin by defining economic development, which goes beyond just money and includes factors like education, healthcare, and access to opportunities, all crucial for a nation's growth.
1.2 Happiness: Exploring happiness as more than a fleeting emotion, we consider it as a long-term state of well-being, encompassing satisfaction with life, a sense of purpose, and positive emotions.
Chapter 2: The Relationship Between Economic Development and Happiness
2.1 Positive Correlations: Examining instances where economic development leads to increased happiness, focusing on improved living standards, access to education, and better healthcare contributing to people's well-being.
2.2 Challenges and Disparities: Acknowledging that economic development doesn't guarantee happiness for everyone, discussing disparities, and investigating the challenges, such as income inequality and social disparities, that may hinder happiness.
Chapter 3: Beyond GDP: Alternative Measures of Progress
3.1 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Limitations: Recognizing the limitations of relying solely on GDP as a measure of a nation's success, exploring alternative indicators that consider happiness, well-being, and sustainability.
Chapter 4: Policy Implications
4.1 Holistic Approaches: Highlighting the importance of crafting policies that prioritize not only economic growth but also social and environmental factors, promoting a more balanced and sustainable development.
4.2 Inclusive Policies: Addressing the need for inclusive policies that ensure the benefits of economic development are distributed equitably, fostering a sense of community and shared prosperity.
Chapter 5: Individual Perspectives
5.1 Personal Well-Being: Considering how individuals perceive and experience happiness in the context of economic development, emphasizing the role of personal relationships, mental health, and work-life balance.
Chapter 6: Conclusion
6.1 Balance and Integration: Summarizing the key findings and emphasizing the importance of finding a balance between economic development and the well-being of individuals and communities.
6.2 Recommendations: Providing recommendations for policymakers, urging them to consider holistic approaches that integrate economic development with the broader spectrum of factors influencing happiness.
In conclusion, this thesis aims to contribute to a broader understanding of the intricate relationship between economic development and happiness, offering insights and recommendations to inform policies that lead to not only financial prosperity but also a more content and fulfilled society.
Racism in schools and colleges
This thesis delves into the pressing issue of racism in schools and colleges, aiming to unravel its complexities and shed light on the importance of creating educational spaces that are free from discrimination. In simple language, this research seeks to empower educators, administrators, and policymakers with knowledge to foster inclusive learning environments.
Chapter 1: Recognizing Racism in Educational Settings
1.1 Definition: Starting by defining racism, we explore how it manifests in schools and colleges, including overt acts and more subtle, systemic forms of discrimination.
1.2 Prevalence: Highlighting the prevalence of racism in educational institutions and acknowledging its impact on students, staff, and the overall learning environment.
Chapter 2: Impact on Students
2.1 Academic Achievement: Discussing how racism can affect academic performance and hinder the educational success of students from marginalized communities.
2.2 Mental and Emotional Well-being: Examining the emotional toll of racism on students, considering its impact on mental health, self-esteem, and a sense of belonging.
Chapter 3: Institutional Racism
3.1 Systemic Bias: Unpacking the concept of institutional racism, exploring how policies, practices, and curriculum can perpetuate inequalities within educational systems.
3.2 Disparities in Discipline: Addressing racial disparities in disciplinary actions and consequences, highlighting the need for fair and equitable disciplinary practices.
Chapter 4: Promoting Inclusivity
4.1 Diversity in Curriculum: Advocating for a diverse and inclusive curriculum that reflects the experiences and contributions of individuals from various racial and ethnic backgrounds.
4.2 Culturally Competent Teaching: Emphasizing the importance of culturally competent teaching practices that consider and respect the diverse backgrounds of students.
Chapter 5: Creating Safe Spaces
5.1 Anti-racism Education: Discussing the role of education in combating racism, promoting anti-racist practices, and fostering a culture of inclusion and acceptance.
5.2 Community Engagement: Highlighting the significance of involving parents, communities, and stakeholders in creating a collaborative effort to address racism in schools.
Chapter 6: Conclusion
6.1 Call to Action: Summarizing key findings and issuing a call to action for educators, administrators, and policymakers to actively work towards eradicating racism from educational institutions.
6.2 Vision for the Future: Envisioning a future where schools and colleges serve as models of inclusivity, where every student feels valued, respected, and has equal opportunities to thrive.
In conclusion, this thesis contributes to a broader understanding of racism in schools and colleges, providing actionable insights for educators, administrators, and policymakers to work collectively towards fostering environments that are truly inclusive and equitable.
Impact of AI on Future
This thesis explores the impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on our future, aiming to demystify this rapidly advancing technology and its potential effects on society. Written in simple language, this research seeks to inform the general public and policymakers about the transformative nature of AI and how it may shape our future.
Chapter 1: Unveiling the Power of AI
1.1 Definition: Beginning with a clear definition of AI, we explore how machines can be trained to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
1.2 Evolution of AI: Tracing the development of AI from its beginnings to the present, showcasing its growth and increasing presence in our daily lives.
Chapter 2: Transforming Industries
2.1 Automation: Discussing how AI-driven automation is transforming industries, impacting jobs, and reshaping the nature of work.
2.2 Innovation: Highlighting the role of AI in fostering innovation, from healthcare to finance, and its potential to address complex challenges.
Chapter 3: Enhancing Everyday Life
3.1 Personal Assistants: Exploring how AI-powered personal assistants and smart devices are becoming integral parts of our daily routines, simplifying tasks and enhancing convenience.
3.2 Healthcare Advancements: Examining the potential of AI in healthcare, from diagnostics to personalized treatment plans, and its impact on improving patient outcomes.
Chapter 4: Ethical Considerations
4.1 Bias and Fairness: Addressing concerns related to AI bias and the importance of ensuring fairness and equity in AI systems.
4.2 Privacy and Security: Discussing the ethical considerations around AI and the need for robust measures to protect individual privacy and data security.
Chapter 5: Education and Skills
5.1 Reskilling: Highlighting the importance of education and skills development to prepare individuals for the changing job landscape influenced by AI.
5.2 Access to Opportunities: Discussing the role of policymakers in ensuring equitable access to AI-related opportunities and resources.
Chapter 6: Future Scenarios
6.1 Possibilities: Exploring potential future scenarios shaped by AI, from advancements in scientific research to addressing global challenges.
6.2 Challenges: Addressing challenges and uncertainties associated with AI, emphasizing the need for responsible development and regulation.
Chapter 7: Conclusion
7.1 Informed Decision-Making: Summarizing key points and emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making by policymakers and individuals to harness the positive impact of AI while mitigating potential risks.
7.2 Coexistence with AI: Encouraging a vision of a future where humans and AI coexist harmoniously, with technology serving as a tool for progress and enhancement.
In conclusion, this thesis contributes to a broader understanding of the impact of AI on our future, providing insights and considerations for the general public and policymakers to navigate the evolving landscape of AI with awareness and responsibility.