Overview
With the intention of providing an assessment plan to the nurses for determining the dependence and independence of patients in the hospital, Roper Logan and Tierney's Model of Reflection was created. This model was developed in the year 1980 and was named after the author of the model of reflection, Nancy Roper, Winifred W. Logan, and Alison J. Tierney.
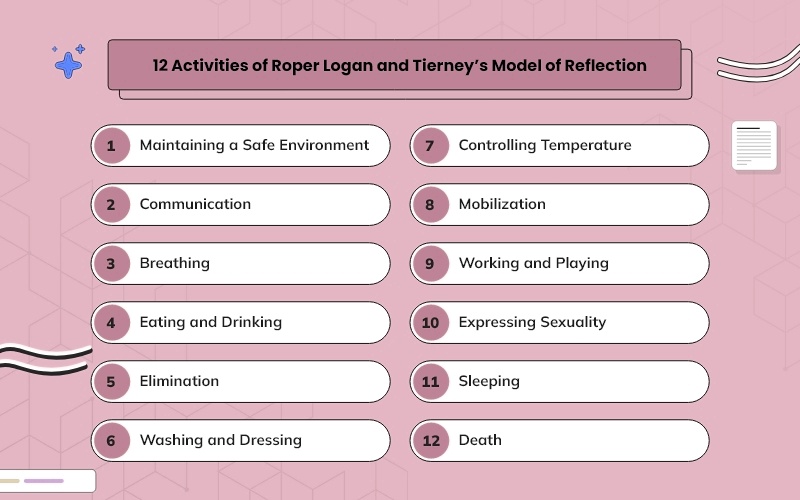
12 Activities of Roper Logan and Tierney’s model of reflection
Through the model, the author proposed 12 activities of daily living that state.
- Maintaining a safe environment
- Communication
- Breathing
- Eating and drinking
- Elimination
- Washing and dressing
- Controlling temperature
- Mobilization
- Working and playing
- Expressing sexuality
- Sleeping
- Death
These 12 activities will act like an action plan for nurses that take care of the patients in the hospital. These factors will assist the nurses in checking the dependency or independence of the patient over the hospital. Moreover, these action plans would also assist hospitals in analyzing the progress report of the patient from time to time. This will not only assist in keeping track of the patient’s performance but will also assist in measuring the performance of your key performance indicators.
Moving ahead, Logan also stated that all the above-stated activities are majorly influenced by 5 major factors. He stated that if these mentioned factors are not taken into consideration, they might result in biased or not well-informed results. The 5 factors stated by Roper Logan and Tierney's model of reflection are
Five Factors affecting 12 activities
1. Biological
The biological factors consist of the overall condition of the patient. To elaborate, it includes the information about the medical condition of the patient before they contacted the hospital for the diagnosis. This factor is important because based on the biological condition of the patient, you will be able to make a well-informed decision about the treatment and medication.
2. Physiological
As per Roper Logan, this section is all about “knowing, thinking, hoping, feeling, and believing.” This implies that this section will cover all the emotional contexts of the patient that will impact the further treatment in one way or another.
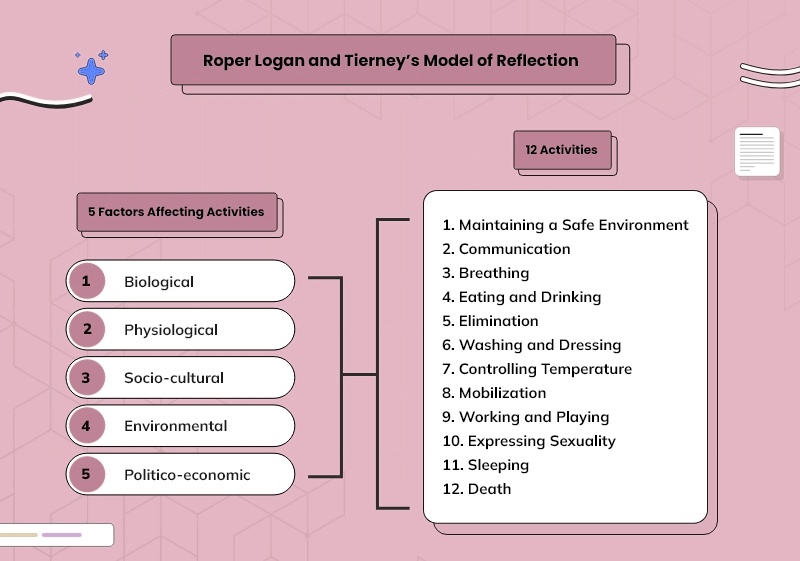
3. Socio-cultural
The impact of the culture and society on the patient will be under the category of social culture factor that impacts the result of the overall action plan. This section is related to the cultural beliefs, values, and traditions that affect the patients in some possible way.
4. Environmental
This impacting factor deals with the environmental impact on the activities that will be carried out with the patient. This states that a change in environment or unfavorable environment can impact the overall performance or progress of the patient.
5. Politico-economic
Last but not least come different politico-economic factors that might impact the activities. This can include various factors such as the state of war within the country, funding policies or schemes launched by the government, or additional economical benefits due to health insurance.
References
Kany, S., Vollrath, J.T. and Relja, B. (2019) “Cytokines in inflammatory disease,” International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), p. 6008. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236008.
Roberts, A., Agnew-Blais, J., Spiegelman, D., Kubzansky, L., Mason, S., & Galea, S. et al. (2015). Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Sample of Women. JAMA Psychiatry, 72(3), 203. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2014.2632